Describe a Transformation Using Two.unique Transformation
When it is done in both directions the increase or decrease in both directions need. Jul 19 2018.

Quadratic Parabola Function Graph Transformations Notes Quadratic Functions Quadratics Graphing Parabolas
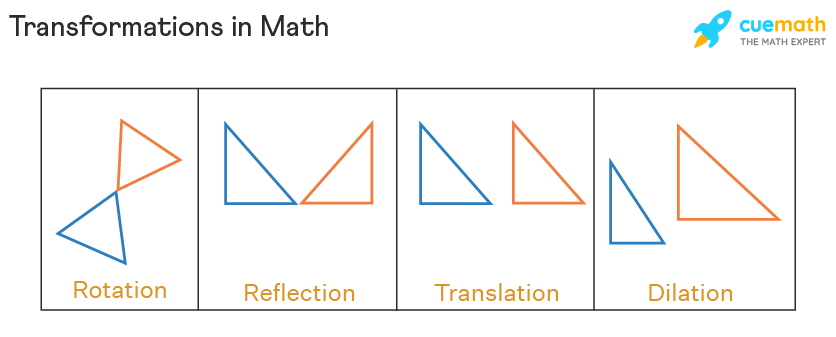
Identify Transformations Learn to identify transformations of figures.

. After that the shape could. Translation is an example of a transformation. The horizontal shift is described as.
Horizontal transformation or translation on a function. - The graph is shifted to the right units. The horizontal shift depends on the value of.
Transformation Rules on the Coordinate Plane. X y x a y b Reflection across the x-axis. Describe the Transformation The transformation being described is from to.
Scaling is the concept of increasing or decreasing the size of a picture. These are what mathematicians call. Each point moves a units in the x-direction and b units in the y-direction.
A translation moves a shape up down or from side to side but it does not change its appearance in any other way. Let H be the plane x 2 y 3 z 0 let N be the line N Span 1 2 3. During bungee jumps gravitational potential energy is converted to elastic potential energy.
When a transformation takes place on a 2D plane it is called 2D transformation. In one or in either directions. Measure the distance from the centre of enlargement to a point vertex and then use the scale.
The geometric transformation is a bijection of a set that has a geometric structure by itself or another set. 1 Find the standard. A rotation followed by a translate followed by a scale will not give the same results as a translate followed by a rotate.
The transformation that can be used to transform f x to g x is T 2 - y12 x 0 2 Another transformation that can be used is to rotate f x by the vertex angle as follows. We can have various types of transformations such as translation scaling up or down rotation shearing etc. Two dimensional shapes are rarely found in isolation in the real world but are repeated reflected translated and rotated.
When we transform or translate a graph. Describe at least three. In this example the scale factor is 15 since 2.
R 3 R 3 be the transformation T x y z 13 x 2 y 3 z 10 y 2 x 6 z 5 z 3 x 6 y. If we start with a straight line with slope one in order to get the. In this case which means that the graph is not.
Stretching or scaling shifting and flipping. Here are some figures and their images under transformations. Plants convert light energy to chemical energy through photosynthesis.
To perform a dilation just multiply each side of the preimage by the scale factor to get the side lengths of the image then graph. Draw ray lines through the centre of enlargement and each of the vertices of the original shape. Then turn it 90 cw.
We have three transformations that wed normally use. Follow the steps below to observe some real life examples of energy transformation then create two on your own. In this lesson we will look at how to identify the different types of transformations.
For now well focus on two transformations. When you do multiple transformations the order makes a difference. In each case the original figure shaded is transformed to its image outline only by some transformation.
Using Transformations in Designs Pathway 1 Leaps and Bounds eg 1. Start with the quadrilateral at top left. Slide it to the right to get the 2nd shape on the top.
If a shape is transformed its appearance is changed. - The graph is shifted to the left units.
Transformations Types Rules Formulas Graphs Examples

Transformations Types Rules Formulas Graphs Examples

Transformations Unit Reflections Geometry Interactive Notebook Reflection Geometry Geometry Interactive Notebook Translations Math
No comments for "Describe a Transformation Using Two.unique Transformation"
Post a Comment